Getting Started
The visuals of the TIT terminal emulator are modeled after the KDE Konsole. It’s the KDE flavored terminal. Shortcuts and information shared on this wiki are generally applicabale to all linux terminal emulators.
The current user
When you open a new terminal window, probably the first thing you will see is your username and your PC name.
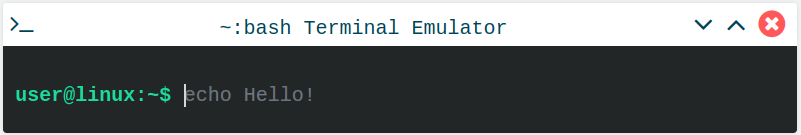
In this example screenshot from TIT, the username is called user and the PC name is linux.
To change between users use the su command.
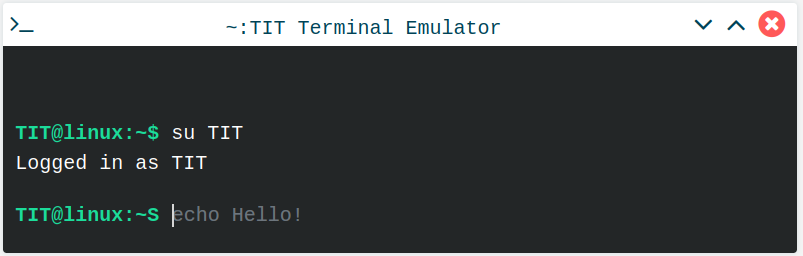
User permissions
Some actions such as installing new applications, updating packages, modifying system files require admin or SuperUser permisions. The superuser has ultimate control and can do anything. It is extremely powerful so be sure to not leak your passwords!
Executing a command as admin
To execute a command with admin privileges, simply write sudo before your command. In most cases you will be prompted to enter the password for the current
user. After entering your password, your command will be executed.
Example:
sudo echo I am the super user B)
This command will print the text
I am the super user B)to the terminal.sudomeans that it has been executed as an admin.
Command history
You can use Up Arrow and Down Arrow to quickly preview your previously executed commands. This is a handy shortcut to re-enter long, and previously entered commands.